Choosing energy efficient sliding doors is crucial for any homeowner. These doors not only enhance aesthetics but also play a significant role in energy conservation. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, energy-efficient doors can save homeowners as much as 15% on heating and cooling costs. This translates to substantial savings over time.
Opting for energy efficient sliding doors means considering materials, insulation, and performance ratings. Advanced technologies, like low-E glass, provide better thermal insulation. However, many homeowners overlook these details. They may focus more on design rather than function. Neglecting efficiency can lead to increased energy bills and discomfort.
Moreover, a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory suggests poor door selection can waste up to 30% of household energy. Many buyers find it challenging to balance style and energy efficiency. It's not simply a matter of aesthetics; it’s about creating a sustainable living environment. Understanding these aspects can ensure you make a choice that benefits both your home and the planet.

When selecting sliding doors, energy efficiency ratings are vital. These ratings indicate how well a door insulates and prevents energy loss. Look for doors with energy ratings provided by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC). They offer clear metrics that guide consumers.
Research shows that homes can lose up to 30% of their heating and cooling energy through inefficient doors. Using ENERGY STAR certified sliding doors can reduce energy costs by up to 12% annually. Make sure to check the U-factor and solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC). A lower U-factor means better insulation. A proper SHGC helps regulate heat from the sun.
Consider the material as well. Vinyl and fiberglass create better seals than wood. Air leakage can bypass even the best energy ratings. Testing often reveals unexpected gaps. Regular maintenance may be needed to ensure optimal performance. Choosing the right sliding door is not just about aesthetics. It directly impacts comfort and utility costs in your home.
When selecting energy-efficient sliding doors, it’s essential to understand the various types available on the market. One popular option is double-glazed doors, which feature two layers of glass with a gap in between filled with inert gas. This design can reduce heat transfer by up to 50% compared to single-pane doors, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Another option is Low-E glass doors, which have a special coating that reflects infrared light, keeping your home cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter.
Wood-clad sliding doors combine aesthetics with efficiency. These doors have a robust wood exterior that adds elegance while providing an insulating layer. Although more expensive, the investment can lead to significant energy savings over time. Fiberglass sliding doors also offer durability and excellent insulation. They resist warping and require less maintenance, making them an appealing choice for many homeowners.
Tips: Look for ENERGY STAR certified products. This certification ensures that the doors meet strict energy efficiency guidelines. Pay attention to the U-factor, which indicates heat transfer. A lower U-factor means more efficiency. Consider professional installation; poor sealing can undermine energy savings. Lastly, reflect on specific needs for your climate. A door that works well in one area might not be suitable for another.
| Type of Sliding Door | Material | Energy Efficiency Rating | Estimated Cost ($) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Sliding Door | Vinyl | U-factor: 0.30 | 800 - 1200 | Low maintenance, excellent insulation |
| Aluminum Sliding Door | Aluminum | U-factor: 0.35 | 900 - 1300 | Durable, lightweight, sleek look |
| Fiberglass Sliding Door | Fiberglass | U-factor: 0.25 | 1200 - 1600 | High insulation value, resistant to warping |
| Wood Sliding Door | Wood | U-factor: 0.28 | 1000 - 1500 | Natural look, customizable, good insulation |
| Composite Sliding Door | Composite materials | U-factor: 0.24 | 1100 - 1500 | Energy efficient, moisture resistant |
When selecting sliding doors for your home, energy efficiency is paramount. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, windows and doors account for about 30% of residential heating and cooling energy use. This emphasizes the need to choose doors that minimize heat transfer. Look for options with Low-E (low emissivity) coatings. These can reduce heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter, making your home more comfortable year-round.
Another factor is the material. The Energy Star program suggests vinyl and fiberglass options are often more energy-efficient than traditional wood. However, they might lack the natural aesthetic of wood. Consider how much you value energy efficiency versus traditional style. Additionally, check the door's air leakage rating. Even well-insulated doors can lose efficiency if they do not seal properly. A tight seal means comfort and savings.
Many sliding doors now feature double or triple glazing. This improves insulation significantly. However, the trade-off might be cost. Investing in high-quality sliding doors can be expensive upfront but pays off in lower energy bills. When evaluating all these factors, it's essential to find a balance between aesthetics, efficiency, and budget. Sometimes, the best choice isn’t the most obvious one.
This bar chart illustrates the energy efficiency ratings of various types of sliding doors, ranging from single pane to gas-filled options. The ratings help homeowners understand which door types are more energy-efficient, aiding in better decision-making when selecting sliding doors for their homes.
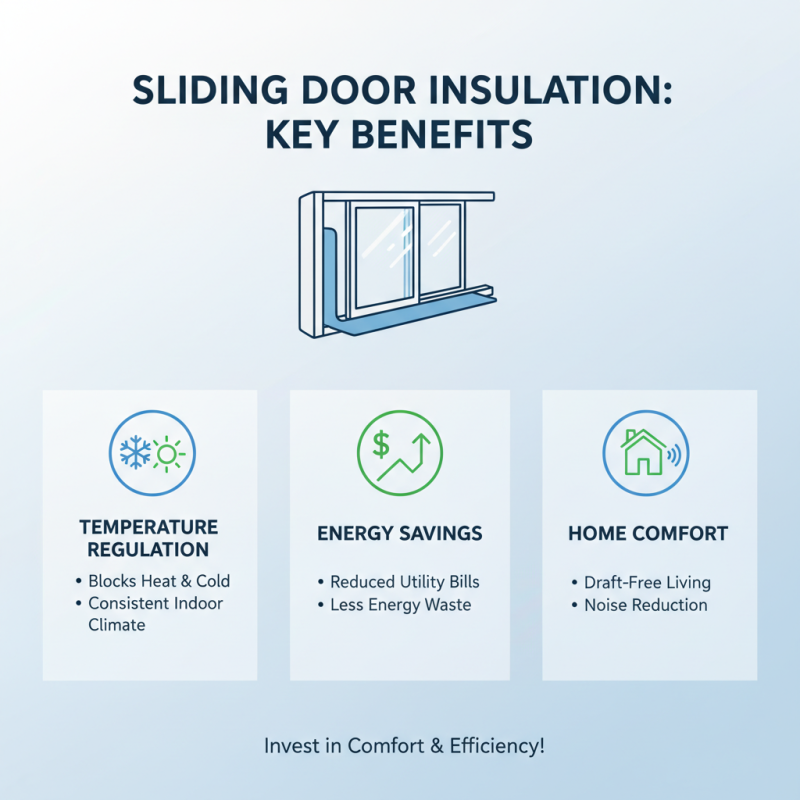
Insulation plays a vital role in the design of sliding doors. Proper insulation reduces energy loss, keeping your home comfortable. It prevents outside temperatures from affecting your indoor climate. Poorly insulated doors can lead to higher energy bills. That’s frustrating. You might not realize the impact until it’s too late.
Look for materials that naturally offer good insulation. Double-glazed glass, for example, traps air between layers. This air acts as an insulator. Furthermore, the frame's material matters. Wood and fiberglass typically provide better insulation than metal. However, metal frames can be designed with thermal breaks, adding some value. Is your current choice really efficient?
Weatherstripping is another detail often overlooked. Gaps around the door can leak air. Sealing these gaps helps maintain temperature. Inspect these areas regularly. It’s a simple step that can yield significant benefits. Small changes can lead to noticeable differences. Are you considering insulation on your sliding doors? Think about it.

When it comes to installing sliding doors, maximizing energy efficiency is key. Choose doors with high-performance glazing. Low-E glass can reduce heat transfer, keeping your home cooler in summer and warmer in winter. Studies show that low-E glass can increase energy efficiency by up to 20%. This is significant, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
Proper installation also plays a vital role. Ensure a tight seal around the frame to prevent drafts. Gaps can lead to energy loss and discomfort. In fact, air leaks account for an estimated 30% of energy waste in homes, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Use weather stripping to enhance insulation. This small detail can make a big difference in energy bills.
Additionally, consider the orientation of your sliding doors. South-facing doors can harness natural sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. However, too much sunlight can heat up your home. Balance is crucial. Proper shading devices can help. Reflect on how your choices impact your home’s energy efficiency. Each small improvement can contribute to a warmer, more economical living space.






Opening Hours
Monday: 8:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Tuesday: 8:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Wednesday: 8:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Thursday: 8:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Friday: 8:00 AM – 4:00 PM
Saturday: Closed
Sunday: Closed
